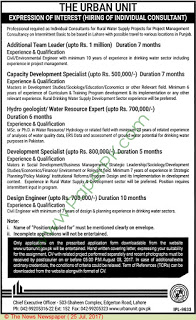
Fineness of cement is a characteristic property of cement that signifies the particle size of cement and its specific surface area. Greater fineness of cement means the particles are finer and had more surface area. In case of very coarse cement, under some conditions it can cause a serious bleeding problem on some construction projects.
There are already many research articles in journals and research papers that have discussed the effect of fineness of cement on concrete and here I have summarized those research papers to give you an overview of the variations and effects the fineness of cement cause on the properties of concrete.
- Increased Rate of Hydration
- Reduction in Bleeding
- Increased Modulus of Elasticity
- Increased drying shrinkage
- Decreased effect of Freezing and Thawing
- Decreased detrimental effects
- Water Requirement
Increased Rate of Hydration
The rate of hydration depends directly on the fineness of the cement as finer cements offer greater surface area for hydration to take place, and for rapid development of strength, high fineness is necessary. But higher rate of hydration means higher rate of early heat evolution.
Reduction in Bleeding
Increasing the fineness of cement reduces the amount of bleeding in concrete by increasing the water requirement of concrete.
Increased Workability
The workability of non-air-entrained concrete is increased by increasing the cement fineness. The workability of non air-entrained concrete is increased by increasing the cement fineness. In air-entrained concrete the effect of fineness of cement on workability is very much less pronounced.
Increased Modulus of Elasticity
The 28-day compressive strength & modulus of elasticity of concrete, with or without entrained air, increases with an increase in cement fineness. The difference in compressive strength due to difference in fineness of cement is considerably less at 1 year\’s age.
Increased Drying Shrinkage
The fineness of cement influences the drying shrinkage of concrete. When the water content is increased because of fineness, the drying shrinkage is increased. However, if excessive bleeding due to coarseness of the cement takes place, a reduction in the drying shrinkage occurs.
Decreased Freezing and Thawing
The resistance of air-entrained concrete to deterioration caused by freezing and thawing decreases with an increase in cement fineness. The same trend is noted with non air-entrained concrete, but to a lesser degree.
Like Us on Facebook!
Decreased Detrimental effects
Both air-entrained and non air-entrained concrete containing 100 percent reactive aggregate are detrimentally affected by increased expansion at all ages by increases in the fineness of a high-alkali cement.
Subscribe Us on YouTube!
Water Requirement
Increasing the fineness of cement from 2700 to about 4000 cm2/g reduces the water requirement of concrete. Increasing the fineness of cement beyond an optimum limit increases the water requirement of concrete.