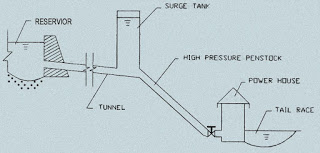
In a hydroelectric plant, the flow of water to a turbine must be decreased rapidly whenever there is a sudden drop in load. This results in high water-hammer pressures and may need a very strong and hence expensive pipe. Surge chambers are used to handle this situation. Typical Definition for a surge chamber can be :-
A surge chamber is a vertical standpipe connected to the pipeline (Figure). With steady flow in the pipe, the water level zl in the surge chamber is below the static level (z=0).
 |
| What is a Surge Chamber in a Hydropower Project? |
When the valve is suddenly closed, water rises in the surge chamber. The water surface in the tank will fluctuate up and down damped out by fluid friction.
Surge chambers are usually open at the top and of sufficient height so that they will not overflow. In some instances they are permitted to overflow if no damage will result.
The surge chamber, in the event of a sudden demand for increased flow, provide some excess water, and the entire mass of water in a long pipeline is accelerated.
Purpose of Surge Chamber
- When the load decreases, the water moves backwards and get stored in it.
- When the load increases, additional supply of water will be provided by surge chamber.