While we’re talking about “Grouting vs Vitrification”; we’re comparing two of the most common methods used to fill gaps and crannies. While the grout is a mixture of cement, sand, water, and admixtures is typically used to fill gaps or crevices. Vitrification, on the other hand, is a process involves use of porcelain or stoneware heated and melted to fill such gaps.
Both methods have got their own pros and cons and so it’s always good to compare grouting vs vitrification.
Understanding Grouting
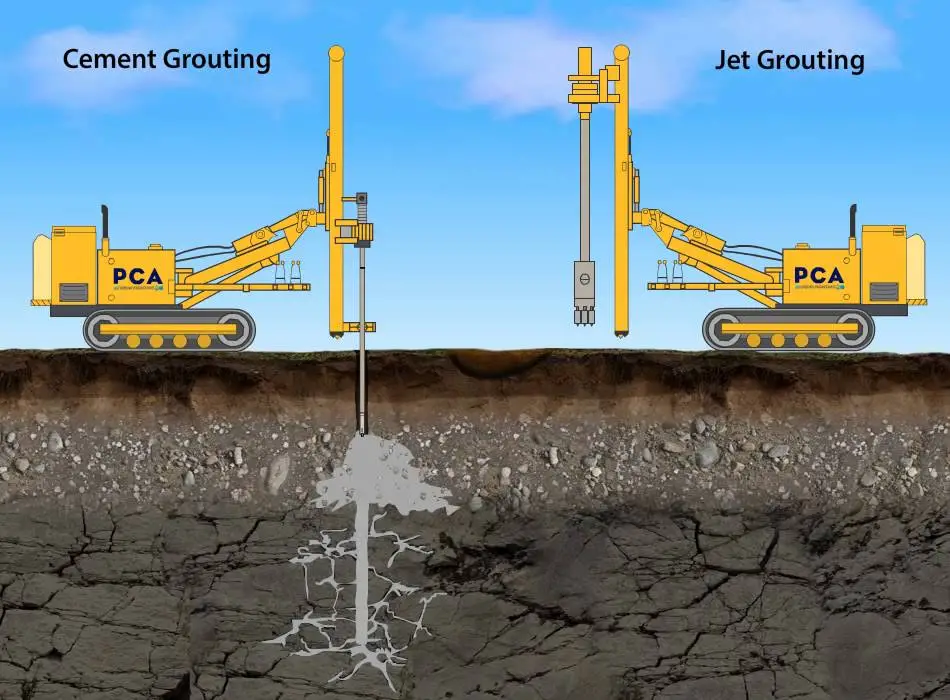
Grouting is a technique that involves injecting a fluid mixture, known as grout, into the subsurface or structures to improve their stability and/or prevent any water leakage or damage.
The grout typically consists of cementitious materials, such as Portland cement or bentonite, mixed with water or other additives. Grouting creates a solid matrix that encapsulates contaminants, reducing their mobility and preventing their release into the environment.
Understanding Vitrification
The term “Vitrification” has been derived from the Latin word “vitreum” that means glass. So, in ceramics; it’s the process where ceramic products are put together with the help of molted glass. Solid ceramics comprises of continuous zone of amorphous. It consists of little grains that are in large number compressed together with bonds.
During Vitrification, these linkages are molted and so all the micro-cracks and voids are filled to make them less permeable to water.

Application of Grouting
Grouting is a versatile technique used in various applications, including:
- Ground Stabilization: Grouting is employed to improve the stability of soils, rock formations, and underground structures. It can fill voids, fractures, or cavities within the subsurface, enhancing the overall integrity and load-bearing capacity.
- Improve the foundation stability of a building or structure.
- Use a gap filler for tiles
- Fixing concrete cracks
- Stabilization of soil – Consolidation grouting
- Contaminant Containment: Grouting is commonly used to contain and immobilize contaminated soil or groundwater. By injecting grout around the contaminated area, it forms a barrier that restricts the movement of pollutants, preventing their spread to adjacent areas or water sources.
- Structural Reinforcement: In civil engineering, grouting is employed to reinforce foundations, tunnels, dams, and other structures. It fills gaps or voids, strengthens weak areas, and enhances structural stability.
Properties of grout
A grout if a viscous non-shrink liquid that hardens in a short time giving a water-tight seal that’s ideal for water retaining structures or foundations. It is available in a pre-mix type but it can also be mixed at-site with grout mixing plant.
- The ingredients of a grout are readily available.
- The premix type grout requires water to be mixed to suit site condition and viscosity requirements.
- The density and the viscosity of the grout shall be as per the mix design requirements.
- Unlike concrete, grout doesn’t have issues like segregation and/or bleeding. You can easily pump or pour grout without the requirement of maximum pour height.
- It offers good consistency and there’s no issue with compaction or consolidation.
- It also offers good adhesion properties resulting in strength development at a rapid rate.
Pros and Cons of Grouting
Grouting offers several advantages:
Like Us on Facebook!
- Versatility: Grouting can be adapted to a wide range of subsurface conditions, making it suitable for diverse geological formations and site-specific requirements.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Grouting is generally a cost-effective solution, particularly for large-scale projects. The availability of grouting materials and equipment makes it a practical choice in many remediation scenarios.
- Ease of Implementation: Grouting techniques are relatively straightforward to implement, requiring standard equipment and experienced personnel.
However, grouting also has limitations:
Subscribe Us on YouTube!
Limited Waste Types: Grouting is not suitable for all types of waste. It is more effective for contaminants that are susceptible to solidification or encapsulation.
Durability: The stability of grout matrix defines its long term durability. Different governing external factors determines the effectiveness over time like material degradation and ground water table chemistry.
Vitrification
The term vitificaiton is mostly used in Ceramics. In a typical kiln, clay bodies are burned to form a liquid viscous paste with higher density. In pottery, these clay-made products are either vitrified or glazed to make them water-resistant or water-tight.
Without glazing or vitrification, the clay products or potery products are weak and they also let microorganisms to grow in the micro cracks and gaps inside.
Most common products of vitrification include porcelain, bone china, and sanitaryware products.
It is worth mentioning, that sanitaryware products are water-tight even without sealing or glazing.




















