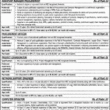
WBM is an acronym for water bound macadam road which is a conventional method for constructing base course layer of a flexible pavement or road. The base course takes position above the granular sub-base or GSB. In a typical WBM base course, stone aggregates are laid along with binder on the top at the time of construction.
The composition of WBM base course includes crushed stones (called macadam). These stones include two sizes i.e. coarser and finer. The small stone and saw dust usually fills the gap to make a dense layer. The water is applied to enhance compaction that is done with compacting rollers.
Construction of WBM road
In a typical composition, three constituents are required to build a WBM road:
- Coarse aggregate
- Filler aggregate or material
- Binding material
- Water
Coarse aggregate: Coarse aggregate is a granular material, typically made of crushed stone, gravel, or slag, that forms the base layer of a WBM road. It provides the structural strength and load-bearing capacity of the road. The size and shape of the coarse aggregate particles are important factors in determining the strength and durability of the road.
Filler aggregate or material: Filler aggregate, also known as fine aggregate, is a material that is added to the road to fill any voids between the coarse aggregate particles. This can be made of crushed stone, sand, or other materials. The filler aggregate helps to improve the stability and smoothness of the road surface.
Binding material: The binding material, also known as the bituminous binder, is a hydrocarbon-based material that is used to hold the coarse and filler aggregate particles together. This is typically asphalt cement, which is heated and mixed with the aggregate to form a cohesive mixture. The binding material also provides waterproofing and resistance to wear and tear.
Water: Water is also an important component of WBM road construction, as it is used to mix and compact the aggregate and binding material. The water helps to distribute the binding material evenly throughout the aggregate, and also aids in the compaction process to ensure a strong and stable road surface.
Construction procedure of water bound macadam road
Preparation of the foundation: The first step in constructing a WBM road is to prepare the subgrade or base course for the required grade and camber. This includes filling and compacting any potholes or depressions in the surface of the road.
Lateral confinement: Before laying the aggregates, shoulders are constructed to a thickness equal to that of the compacted WBM layer. These shoulders are made of a proper quality of murum or earth and are designed to keep the road surface in place and make it easier to lay the course aggregates.
Like Us on Facebook!
Spreading of course aggregates: Once the shoulders are constructed, the course aggregates are spread uniformly on the prepared base. The number of layers and thickness of the WBM road depend on the details of the pavement design.
Subscribe Us on YouTube!
Rolling operation: The course aggregates are then compacted through rolling operation, which is typically done with the help of 3-wheeled power rollers or vibratory rollers. Skilled operators are necessary to ensure proper compaction and avoid corrugations, uneven finishes and premature wear on the road.
Application of screenings: After the rolling operation is finished, screenings are applied to fill any remaining voids between the aggregate particles. The screenings are applied in multiple layers, compacted and broomed to remove any uncompacted material.
Sprinkling of water and grouting: After the application of screenings, the road surface is sprinkled with water and broomed to ensure the wet screenings are properly compacted into the voids. Additional screenings and compaction may be necessary if voids are still visible.
Application of binding material: Similar to the application of screenings, the binding material is applied in multiple layers and compacted through rolling operation. The wheels of the roller are also watered to wash out any binding material that sticks to them.
Setting and drying of surface: After the final rolling operation, the road is allowed to cure overnight. If any depressions or voids are visible the next day, additional screenings or binding material may be applied and compacted.
Preparation of shoulders: While the road is curing, shoulders are constructed alongside the road by filling earth to the specified cross slope. They are then properly compacted.
Open for traffic: Once the road has properly dried and is free of any depressions, it is opened for traffic. Initially, traffic is distributed evenly over the full width of the road by placing obstacles such as drums or barricades.
Advantages and Disadvantages of WBM road
Advantages of WBM roads include their durability and resistance to weathering, as well as their ability to provide a stable and smooth surface for vehicles. Some disadvantages of WBM road include:
- Expensive to construct
- Need regular maintenance
- Damage from heavy traffic
- Prone to water logging
- Can be affected by heavy rainfall or flooding
Further Read: Asphalt Quantity Calculator for a road, driveway, or highway