|
| 3D Laser Scanning in Construction |
Just like 360 degree panoramas of a building with accurate position for every pixel this process is commonly referred to as a point cloud survey or as light detection and ranging (LIDAR, a combination of the words \’light\’ and \’radar\’).
Emerging of 3D Laser Scanning
Laser Scanning Technology has emerged as a useful tool in documenting existing conditions of buildings. The main application for such documentation is to assess current as-built conditions of existing mostly historical buildings. The technology can also be used as an integral part of construction progress industry.
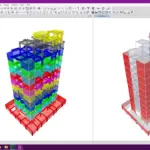
Some of the instruments available in the market comprises of high-speed lasers with integrated camera that uses color coding mounted on a tripod. Such instruments can be operated upto a range of 180 meters and at speeds of upto 990,000 points per second making a cloud. These points are then used to generate 3D imagery which can be converted for use in 3D computer aided design (CAD) modeling or building information modeling (BIM). Most of the CAD and BIM Softwares in market allow their systems to import the point cloud data into 3D visual graphic material.
Applications of 3D Laser Scanning
Whether you\’re delivering scan data of comprehensive as-built documentation, performing comprehensive data analysis or creating a renovation model based on an existing structure or realistic project scheduling or system clash avoidance; laser technology is on its way to become the standard in the Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Virtual Design and Construction (VDC). Laser scanning provides an efficient method for surveying inaccessible surfaces as well as complex geometry.
In the construction industry market we now have contractor that work as virtual design and construction contractors that can run your project virtually on computer simulations from excavation to finishing of a building, the complete outlook of the construction activities involve enhances the planning process thereby completely eliminating the chances of mistakes and errors.
BIM & 3D Laser Scanning
The need of BIM and Laser Technology owes its presences to the fact that on a typical construction project, rework accounts for 12 to 15 percent of the cost of construction. Thus by the introduction of laser technology the rework reduces to 1-3 percent and the ability to catch conflicts before they happen makes laser scanning as a fast emerging need of the industry.
Laser scanners record up to a million of points per second, each with an x,y and z co-ordinate. As scanners work using a line of sight, the scan will only record what you can see, so In order to gain full coverage of a building, multiple scan set-ups need to be taken at various locations.
Laser scanning has proved to be much quicker, more accurate and cheaper than conventional survey measurement. The accuracy of the process depends on the steadiness of the instrument base and the distance from the object. Close range objects achieve sub millimetre accuracy. For normal terrestrial survey work + or – 2mm per 100m is a good guide to accuracy. Greater distances of 2 kms may be accurate to + or – 50mm.
Deterrents to Adoption of 3d Laser Scanning
The technology is still early in the adoption cycle while the 3D scanning market has reportedly grown 25 – 30% over the last five years. Because traditional surveying methods are more cost effective on some projects, it may be difficult to determine when to make the leap to laser scanning.
If a company has not yet adopted designing and constructing in 3D, it may be difficult to “buy-in” to laser scanning. Lastly, like other 3D technologies in the marketplace, there are integration challenges involved with laser scanning.
While the construction industry is often considered to be a slow adopter of new technology, design and construction professionals are challenging themselves to build projects faster and cheaper with the use of technologies like BIM, tablets, and custom-designed apps.
A less publicized technology in the adoption phase is 3D laser scanning. Engineering and consulting firms are recognizing the benefits laser scanning can bring to their clients and operations.
Benefits of Laser Scanning
3D laser scanning benefits for the construction industry far outweigh the added cost. One of its biggest perks is its versatility throughout a project.
Despite slow adoption, 3D scanning currently serves a number of purposes and is used in a variety of industries. 3D scanning uses range from roadway and bridge surveying to process plant maintenance and retrofit projects to bridge and building deformation monitoring. Some areas where 3D scanning is currently in use are discussed further below.
Renovators and other builders are able to utilize 3D laser scanning to create personalized verifications and blueprints in a safer and faster method. Additional uses for builders include:
- Transportation
- Improved Planning & Design
- Building & Infrastructure
- Safety & Regulatory Compliance
- Costing and Scheduling
Transportation
3D Laser scanning finds it application in the construction and maintenance of highway transportation projects including bridges and roadways. With Laser Scanning the highway engineers can do road topography surveying, the horizontal and vertical profiling of the roadway surface, paving volume calculations, intersection surveys, as-builts for bridges, bridge damages assessments and retrofitting and archiving the historical bridges and landmarks. 3D scanning is also utilized in the maintenance and construction of tunnels, airports, rail, and ports and harbors.
Improved Planning & Design
As discussed above the Virtual Design Construction and BIM Model using Point cloud based as-built drawings and 3D models can minimize site clashes by improving design or by evaluating alternative designs prior to construction. The accurateness of dimensions obtained from laser scans can also help improve planning by providing exact measurements for demolition and removal of components, as well as for prefabricated materials, minimizing waste and changes in the field.
Building & Infrastructure
One of the mostly faced snags and difficulties that are encountered during renovation projects is incomplete or inaccurate as-built drawings for an existing building. 3D laser scans can be used to develop accurate 3D models of the interior and exterior of existing buildings, which can aide in planning and designing future additions and renovations.
Safety & Regulatory Compliance
Laser scanning methods are often safer than manual data capture methods and are increasingly being used to help comply with health, safety and environmental imperatives. The remote sensing ability and quick data capture of laser scanners reduces a crew’s exposure to harmful environments. For example, 3D scanning can be used in completing land surveys without the need to stop one car. Furthermore, in nuclear power plants, laser scanning can help reduce the size of and the time crews are exposed to high radiation areas.
Costing and Scheduling
A term associated with the BIM stage 2 is called 5D BIM Models and the 5th dimension in that model is its ability in preparation of Cost & schedule of material and rates. It’s been reported that 3D scanning can reduce total project costs by as much as 5 – 7% and the schedule by as much as 10% on industrial projects.
Further…???
Find here how Malaysia have get benefits from BIM in the Construction of Mass Transit Project a Case study.
Malaysia to Experience Benefits of BIM and Cloud Technology in Mass Rapid Transit Project
References
http://www.itcon.org/papers/2016_14.content.09623.pdf
http://constructrealityxyz.com/test/ebook/LGS_AU_When%20to%20Use%20Laser%20Scanning.pdf